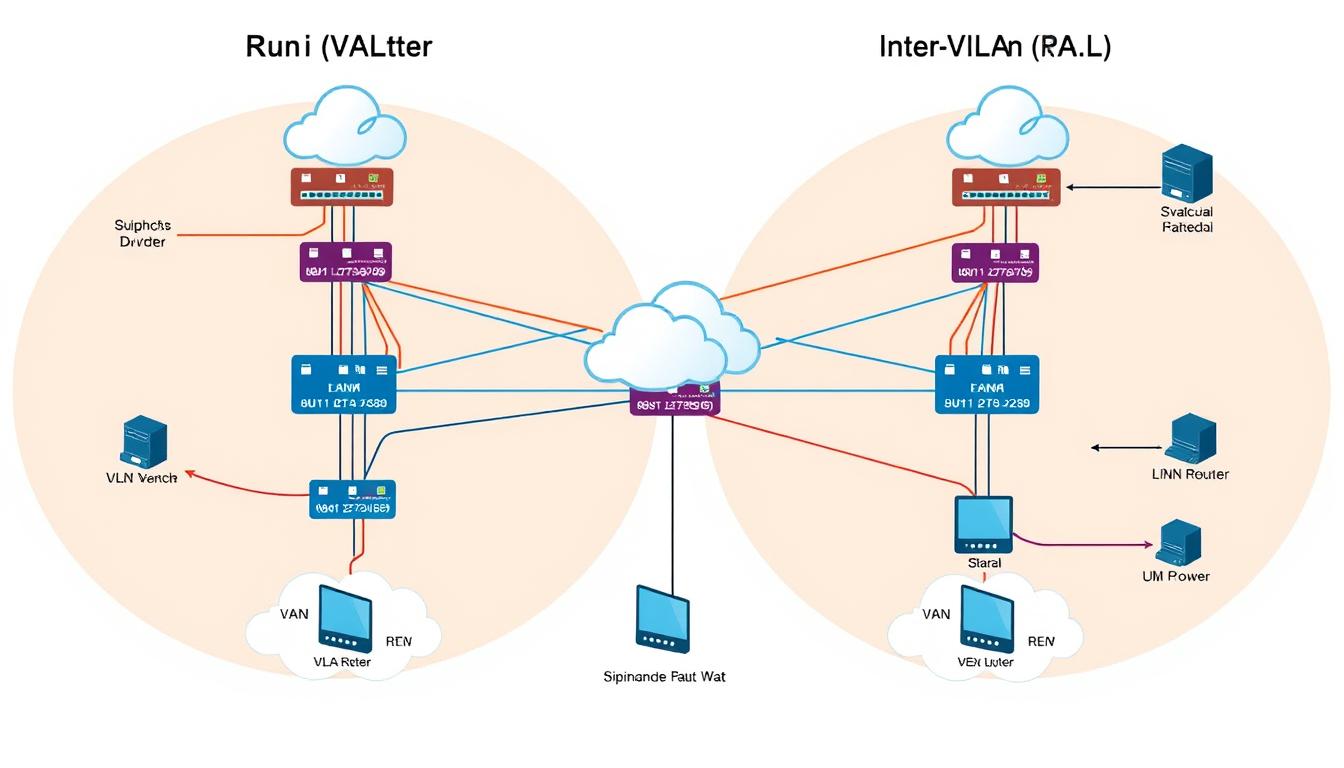
Did you know that about 85% of enterprise networks use VLANs to manage network traffic? This shows how important CCNA VLAN Inter-VLAN Routing is today. As technology grows, knowing about VLANs and inter-VLAN routing is key for Cisco certification. This guide will teach you everything about VLANs, how to route between them, their advantages, and common problems. It’s all to help you succeed in networking.
Introduction to VLANs
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) are key in today’s networking. They help break down big networks into smaller, easier-to-handle parts. This makes it easier to manage and secure your network by keeping traffic in its own lane.
By setting different ports on a switch to different subnetworks, you cut down on unnecessary traffic. This boosts your network’s performance.
Knowing how to set up VLANs is important for good network management. You can have up to 4096 VLANs in an 802.1Q setup. This means you can save money by using one switch for all departments instead of many.
Each VLAN gets its own number, like VLAN 10 for Accounting or VLAN 20 for Marketing. This makes it easy to tell them apart and manage them. With the right setup, each VLAN is its own broadcast domain. This keeps sensitive data safe from people in other VLANs.
But sometimes, devices in different VLANs need to talk to each other. That’s when you need inter-VLAN routing. You might use a router or a Layer 3 switch for this. The right VLAN configuration commands help make sure everything works smoothly.
Understanding the Importance of Inter-VLAN Routing
In today’s networks, inter-VLAN routing is key. It lets devices on different VLANs talk to each other. VLANs help with security and performance but can block communication. Inter-VLAN routing fixes this, making sure data moves well.
Network protocols are vital for inter-VLAN routing. A Layer 3 device is needed for communication between VLANs. Without it, VLANs can’t share resources well, slowing things down. It’s important for departments to access shared resources safely.
VLANs help with network congestion and security. They reduce broadcast domains, improving bandwidth. They also keep sensitive data safe from unauthorized access.
Inter-VLAN routing makes finding network problems easier. It helps pinpoint issues to specific VLANs. This makes fixing problems faster and less disruptive. Using “Router-on-a-Stick” or Layer 3 switches can also boost performance.
In fast-changing environments, VLANs offer flexibility. They make it easy to change the network without physical changes. This meets the needs of today’s organizations. VLAN-specific Quality of Service (QoS) policies help ensure network performance.
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Router-on-a-Stick | Single router interface with subinterfaces for multiple VLANs. | Reduces hardware requirements. | May experience performance bottlenecks during high traffic. |
| Layer 3 Switch | Integrates routing capabilities directly within the switch. | Reduces latency and improves performance. | Generally more expensive than Layer 2 switches. |
| Per VLAN, Per Router Interface | Requires multiple physical interfaces for each VLAN. | Simplifies basic routing. | Can complicate network architecture significantly. |
In conclusion, inter-VLAN routing is vital for network design. It ensures safe and efficient communication between segments. Understanding this is key to making VLANs work best for your network.
CCNA VLAN Inter-VLAN Routing
In the world of CCNA VLAN Inter-VLAN Routing, it’s key to know how to connect different VLANs. This method lets devices on various VLANs talk to each other through special interfaces. You use IP addresses and router sub-interfaces to make this happen. It’s vital for networks to work well together.
Defining Inter-VLAN Routing
A Layer 3 device is needed for inter-VLAN talk. Without it, devices in different VLANs can’t chat directly. For example, VLAN 10 gets the IP range 192.168.1.0/24, with a router sub-interface at 192.168.1.1. VLAN 20 gets 192.168.2.0/24, with a sub-interface at 192.168.2.1. These setups show how routing connects VLANs.
Benefits of Integrating VLANs with Routing
Linking VLANs with routing brings big pluses. Some of these benefits are:
- Enhanced network flexibility: Each VLAN is its own broadcast domain, with its own IP subnet.
- Improved resource utilization: Using “router-on-a-stick” lets you manage many VLANs with one interface, but it has limits.
- Centralized management capabilities: Multi-layer switches make managing networks cheaper and easier, without needing special protocols.
Here’s a table that shows key points about VLAN setup and inter-VLAN routing:
| Feature | Layer 3 Device | Sub-Interface Example | VLAN ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inter-VLAN Communication | Router or Multi-layer Switch | fa0/0.0 for VLAN 10, fa0/0.1 for VLAN 20 | Up to 4096 |
| Default Gateway for Shared Resources | Router Ethernet 0/0 | 192.168.1.1 for VLAN 10 | — |
| Default Gateway for Corporate Devices | Router Ethernet 0/1 | 192.168.2.1 for VLAN 20 | — |
| Protocols Used | 802.1Q, ISL | — | — |
Types of VLANs and Their Functions
Knowing about VLAN types is key for good network segmentation. Each VLAN type has its own role in a network. This improves performance, security, and efficiency. Here, we’ll look at three main VLAN types: Data VLANs, Management VLANs, and Voice VLANs. Understanding these can help you set up VLANs that fit your network’s needs.
Data VLANs
Data VLANs handle user data. They cut down on broadcast domains, reducing network load by up to 30%. This makes networks more efficient, with a 25-40% boost. Plus, setting up Data VLANs is quick, taking about 15-30 minutes per VLAN, which is great for growing businesses.
Management VLANs
Management VLANs are vital for network management. They keep management tasks secure and efficient, stopping unauthorized access. A dedicated Management VLAN makes your network more stable. It’s important to keep VLAN configurations right to avoid problems like VLAN Hopping. A secure Management VLAN strategy is key for protecting your network.
Voice VLANs
Voice VLANs are for VoIP traffic. They make sure voice calls are clear and smooth, even when the network is busy. This is important because voice traffic needs to be prioritized. Voice VLANs improve call quality and make your network run better by keeping voice and data separate.
By knowing about VLAN types and their roles, you can use them to improve your network. This makes your network better for your business.
| VLAN Type | Primary Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Data VLAN | User data traffic | Reduces broadcast traffic, boosts overall efficiency by 25-40% |
| Management VLAN | Network management tasks | Improves security and stability of management protocols |
| Voice VLAN | VoIP traffic | Ensures QoS for clear communications during peak use |
Setting Up VLAN Configuration
Setting up VLANs on Cisco devices is a structured process. Knowing basic network protocols is key. Start by accessing the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI). Here, you’ll use commands to create and manage VLANs.
Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Create a VLAN: Start by defining your VLAN with the command
vlan [VLAN_ID]. Replace [VLAN_ID] with your desired number. - Assign a Name: Naming your VLAN makes management easier. Use
name [VLAN_NAME]. - Assign Ports to a VLAN: Enter interface configuration mode with
interface [INTERFACE_ID]. Then, assign it to the VLAN withswitchport access vlan [VLAN_ID]. - Configure Trunking: For VLANs across multiple switches, set trunk ports with
switchport mode trunk. - Verify Configuration: Check VLAN status and port assignments with
show vlan briefandshow ip interface brief.
Avoid VLAN conflicts by keeping VLAN IDs consistent across your network. For inter-VLAN routing, assign unique IP addresses to sub-interfaces. Use 192.168.X.1 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
VLANs help segment your network for better performance and security. Remember these tips for a successful VLAN deployment:
- Ensure all devices in the VLAN have the same subnet for communication.
- Regularly check and maintain VLAN configurations against network changes.
- Teach your team about VLAN management for better efficiency.
Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Setting up inter-VLAN routing is key for devices on different VLANs to talk to each other. There are three main ways to do this: Traditional Method, Router-on-a-Stick, and Multi-Layer Switch. Each method has its own strengths, helping you pick the best one for your network.
Traditional Method Configuration
The Traditional Method needs a separate router interface for each VLAN. This can get messy as your network grows. For example, with 10 VLANs, you’d need 10 router interfaces. This method can be hard to scale, with about 60% of setups facing issues.
To set it up, you create VLANs, assign them to switch ports, and give each VLAN an IP address on the router. This method can be pricey and hard to manage, mainly in big networks.
Router-on-a-Stick Method Configuration
The Router-on-a-Stick method uses one router interface for many VLANs through subinterfaces. It’s popular, used in about 65% of setups. It saves money by needing fewer interfaces, cutting costs by 30%.
To set it up, you create a trunk link, define subinterfaces for each VLAN, and assign unique IP addresses. For instance, you might set up VLAN 10 with an IP of 10.10.10.1. This method is faster, cutting packet transmission times by 20%.
Multi-Layer Switch Method Configuration
The Multi-Layer Switch Method uses Layer 3 switching for routing inside the switch. This boosts performance by up to 40% over traditional methods. To set it up, you enable IP routing on the switch, assign IP addresses to VLAN interfaces, and check trunking settings.
For example, you might set up VLAN 20 with an IP of 192.168.20.1. This method makes your network handle multiple VLANs well without extra routing devices.
Common Issues in VLAN and Inter-VLAN Routing
It’s important to know about common VLAN issues and routing problems. These can cause network troubles. Spotting these problems early helps keep your network running smoothly.
VLAN Tagging Mismatches
VLAN tagging mismatches are a big problem. When VLANs are deleted or set up wrong, ports stop working. This makes VLANs seem to disappear from trunk outputs.
For example, if a trunk port is set to “shutdown,” VLANs won’t send as expected. Make sure your trunk setup matches your network’s VLANs. Check trunk ports to see if they have the right VLANs.
Routing Loop Problems
Routing loop problems can block communication between VLANs. They often come from wrong routing setups or router subinterface mistakes. If a router’s subinterfaces don’t match VLANs, things break down.
Also, managing DHCP exclusions is key to avoid network conflicts. If VLANs 10 and 20 use the same DHCP range, it causes trouble. Regularly check and adjust your routing table to avoid these issues.
| Issue | Description | Diagnostic Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Missing VLANs | Ports remain inactive until reassigned after VLAN deletion. | Check VLAN configuration on switch, verify port assignments. |
| Switch Trunk Port Issues | Incorrect trunk configuration leads to VLANs not being recognized. | Examine trunk port settings, confirm VLANs allowed on trunk. |
| Access Port Issues | Improper VLAN assignment on access ports can impair connectivity. | Assign ports correctly to the intended VLAN. |
| Routing Loops | Incorrect routing configurations can create infinite loops. | Validate routing tables and subinterfaces for accuracy. |
Practical Tips for Effective VLAN Management
Managing VLANs well means knowing key strategies and best practices. Good VLAN management boosts network performance, security, and organization. The right steps ensure a network that meets industry standards.
Best Practices for VLAN Implementation
There are several best practices for VLAN implementation. These can greatly improve network management. Here are some key recommendations:
- Avoid using VLAN 1 for critical operations. Place important devices in different VLANs for better security.
- Plan VLAN assignments carefully to organize network resources well. Aim for VLAN sizes of /25 or /24 for user separation.
- Keep native VLAN consistency across trunk links to avoid unexpected issues during inter-VLAN routing.
- Use VLANs wisely to follow industry regulations like PCI, HIPAA, and SOX. This ensures necessary segregation and security.
When to Segment Networks Using VLANs
Segmenting networks can improve security and performance. Knowing when to segment networks helps optimize small network efficiency. Here are some scenarios to consider:
- For organizations with about 200 workstations, complex VLAN setups might not be needed. Simpler configurations work well.
- Check bandwidth requirements. Make sure there’s enough Layer 3 bandwidth for effective inter-VLAN routing.
- VLANs can reduce broadcast traffic. This makes a good way to manage resources and access.
- Use VLANs for security. They help manage access and segregate resources, lowering unauthorized access risk.

| VLAN Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Server VLAN | Segregate server traffic from user traffic for improved security. |
| LAN VLAN | Standard local area network segmentation for users. |
| VoIP VLAN | Prioritize voice traffic for better call quality. |
| Print VLAN | Manage printer access within the network. |
| Backup VLAN | Isolate backup traffic to prevent interference with primary operations. |
| DMZ VLAN | Segment traffic to and from public-facing servers to maintain security. |
| WAN VLAN | Connect to wide area networks with appropriate segmentation. |
| Test VLAN | Create isolated environments for testing without impacting live data. |
Conclusion
In this guide, you’ve learned about CCNA VLAN Inter-VLAN Routing and networking basics. You now know how VLANs work and how they’re used with routing. This knowledge is key for setting up networks well.
Configuring VLANs and routing between them is vital for smooth data flow. You’ve seen how to use specific IP ranges for VLANs. This helps manage broadcasts and boosts network security.
Remember, getting Cisco certified means knowing how to avoid common routing problems. This guide has given you the basics to tackle network challenges. You’re ready to handle the complexities of modern networks.
Source Links
- Inter-VLAN Routing Operation (4.1) > Inter-VLAN Routing
- Configure Inter VLAN Routing with Catalyst Switches
- Inter-VLAN Routing: Configuration Examples
- Inter VLAN Routing – learncisco.net
- What is Inter VLAN Routing? Best Explained – 2023
- Understanding VLANs, and Inter-VLAN Routing – Part I
- VLANs and Inter VLAN Routing | Essential for CCNA Success
- Understanding Cisco CCNA InterVLAN Routing: Methods and Necessity
- CCNA Training » InterVLAN Routing Tutorial
- CCNA RnS Article #25: Inter-VLAN Routing
- VLAN AND INTER VLAN ROUTING
- Guide to VLANs: What They are, How They Work, and Why They Matter
- Routing Between VLANs Overview [Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.4 Mainline]
- Inter-VLAN Routing using Layer 3 Switches (4.3) > Inter-VLAN Routing
- Inter-VLAN Routing Configuration – %%currentyear%% Step-by-Step Tutorial
- Configure Inter VLAN Routing with the Use of an External Router
- Inter-VLAN Routing | CCNA Blog
- Troubleshoot Inter-VLAN Routing (4.4) > Inter-VLAN Routing
- Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing
- VLAN Best Practices
- Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing > Inter-VLAN Communication Using an External Router: Router-on-a-Stick
- untitled
- Microsoft Word – 4-IJCSE-01750